Digital Twins Gaining Ground; Intermodal Projects Get Green Light; More Supply Chain News

What’s shaping the future of the global supply chain? Digital twins, disruption mitigation, intermodal investments, and AI, among others.
Make Room for Twins
The popularity of supply chain digital twins is rising. These virtual replicas or simulations of a physical supply chain—created using real-time data and advanced technologies such as the Internet of Things, artificial intelligence, and machine learning—enable organizations to better understand, analyze, predict, and optimize their supply chain processes.
How great is the demand? According to Market.us, the worldwide supply chain digital twin market is projected to reach a value of $8.7 billion by 2033—a compound annual growth rate of 12% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2033.
The increasing complexity of supply chains, the need for greater visibility and control, and the rising demand for predictive analytics in supply chain management is driving the growth in this market, according to the report.
Top Trade Disruptors
While the pandemic is firmly in our rearview mirror, a new batch of disruptions have popped up to challenge the supply chain. The Q1/Q2 2024 Retail Sourcing Report from TradeBeyond outlines the top trade disruptors that are likely to throw a wrench into global sourcing plans and buying decisions in 2024. Here are the key highlights:
- Rate fluctuation: Extreme shipping rate volatility with attacks in the Red Sea have sent shipping rates surging since December, more than doubling the rates on some European lanes and creating substantially longer transit times.
- Looming uncertainty: The shipping crisis has made supply chain disruptions more likely, elevating fears of a return to the bottlenecks, component shortages, and product delays that supply chains endured in recent years.
- Tech spend coming: The pace of digitalization continues to accelerate in retail supply chains, with more than 90% of supply chain managers saying their companies are actively engaged in digital transformation. And 46% of supply chain executives anticipate that AI, cognitive computing, and cloud applications will be their greatest areas of investment in digital operations over the next three years.
- Manufacturing slump: The most recent GEP Global Supply Chain Volatility Index warned of continued downturn in global manufacturing through at least the first quarter of 2024 amid softened demand, especially in Europe.
Mega Money for Intermodal Projects

In a win for intermodal infrastructure, the U.S. Department of Transportation (USDOT) recently selected 37 projects to receive funding through the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law’s Mega and Infrastructure for Rebuilding America (INFRA) grant programs. Several of the projects will boost intermodal infrastructure across the country.
The Mega Program, also known as the National Infrastructure Project Assistance program, funds large, complex projects that are difficult to fund by other means and likely to generate national or regional economic, mobility, or safety benefits. Congress established the program in 2021 through the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law and dedicated $5 billion to the program over five years. The most recent awards were the second round of funding, worth roughly $2 billion.
INFRA is a competitive grant program that provides funding for multimodal freight and highway projects of national or regional significance to improve the safety, efficiency, and reliability of freight movement in and across rural and urban areas. The most recent annual program funding amount is $3.1 billion and the annual award amount is $1.5 billion.
Intermodal projects receiving grants in this round of Mega and INFRA funding include:
- America’s Green Gateway: Pier B Rail Program Buildout, Long Beach, Calif. The project will complete the Pier B On-Dock Rail support facility program by significantly enhancing container-on-rail service to and from the ports of Long Beach and Los Angeles.
- St. Lucie River Railroad Bridge Replacement Project, City of Stuart, Fla. The project will replace the existing 100-year-old St. Lucie River Railroad Bridge with a new double-track structure. By diverting freight traffic to rail, the project will increase safety for marine traffic, decrease the potential for blocked grade crossings and vehicle collisions, and shift single-occupancy vehicles to passenger rail travel.
- East River Berth Replacement Project, Garden City, Ga. The project will replace a port berth and two vessel berths at Georgia Ports Authority’s Port of Brunswick’s East River Terminal and will also reduce greenhouse gas emissions by supporting a modal shift from truck to rail for transporting commodities to the Port of Brunswick.
- Louisiana International Terminal Project, St. Bernard Parish, La. The project will construct a new container terminal on the Gulf Coast for the Port of New Orleans that is not air-draft restricted and can accommodate larger vessels.
Walmart Wings It

The nation’s largest retailer will soon boast the retail sector’s largest drone delivery footprint. Walmart recently unveiled plans to dramatically expand its drone capabilities across the Dallas-Fort Worth metroplex, adding more than 30 municipalities and towns in North Texas.
The expansion will enable the company to reach up to 1.8 million additional households—the most ever by a retailer offering drone delivery in a single market—and cover as much as 75% of the metro area.
Individuals who live within 10 miles of participating stores will be able to order thousands of items, ranging from snacks and beverages to baby wipes and over-the-counter medications, for delivery by drone in 30 minutes or less and potentially in as fast as 10 minutes.
The retail giant is partnering with drone delivery companies Wing and Zipline for the service; both are authorized by the FAA to fly drones beyond the line of sight of operators.
Walmart says it has safely completed more than 20,000 drone deliveries over some two years of test flights.
AI in Transportation: All Talk, No Action?
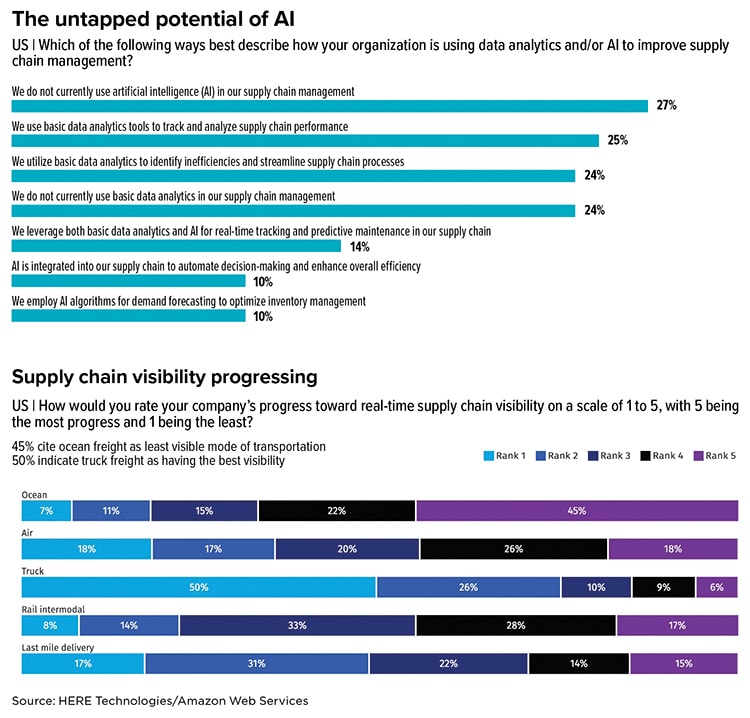
While artificial intelligence (AI) is one of the most buzzed-about topics within the supply chain sector, AI adoption is lacking severely in the U.S. transportation and logistics (T&L) market, according to new data from HERE Technologies and Amazon Web Services. In a multi-country survey of transportation and logistics professionals in the United States, Germany, and the United Kingdom, HERE found a significant gap in the adoption of basic data analytics.
The survey results underscore the untapped potential of AI—from data analytics supported by machine learning to optimized fleet routing, predictive maintenance, and streamlined processes for strategic decision-making.
Here are the report’s key takeaways:
- Only 50% of T&L professionals across the three countries say that their organizations utilize basic data analytics in their operations. At the same time, 25% of all respondents state their organization leverages AI capabilities.
- Cost (23%) is the leading barrier to tech implementation.
- Potential disruption to existing services (12%) and lack of internal expertise (11%) were the second and third most cited barriers to technology implementation.
Somewhat conversely, survey participants were optimistic about their progress toward supply chain visibility, with 86% reporting notable progress toward supply chain visibility and 18% considering their progress significant. Among modes, 50% indicate truck freight has the highest visibility, while 45% cite ocean freight as the least visible mode of transportation (see chart).
Manufacturers: .ru Prepped Against Cyber Attacks?

The manufacturing sector faced an unprecedented 165% surge in cyber attack attempts last year—many coming from Russian and Chinese actors, according to Armis, an asset intelligence cybersecurity company. Its new report reveals that the industry faces severe safety, production, and critical infrastructure risks if security gaps aren’t urgently addressed.
Key highlights include:
- Global attack attempts more than doubled in 2023, increasing 104%. The manufacturing industry weathered a much higher-than-average rate of attacks at a 165% increase.
- In 2023, manufacturing was one of the top industries exposed to attack from Chinese and Russian actors. Compared to other industries, manufacturing experienced an intensified threat landscape, with .cn and .ru domains contributing to an average of 30% of monthly attack attempts.
- The concerning trend of operational technology (OT) devices accessing the internet highlights further potential vulnerabilities, with around 80% of engineering workstations and 60% of supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) servers having internet access over the past year. The vulnerabilities in these devices increase the potential entry points for bad actors.
- Data further highlights a concerning number of exploitable devices owing to usage of end-of-life or end-of-support operating systems that are no longer actively supported or patched for vulnerabilities and security issues by the manufacturer. Additionally, 12% of utilities and 11% of manufacturers are still using legacy operating systems—exacerbating cyber weaknesses.
