Russia-Ukraine Supply Chain Strain
The commodities markets are the industry category that is experiencing the greatest strain as a result of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, according to a Dun & Bradstreet briefing report released in March 2022.
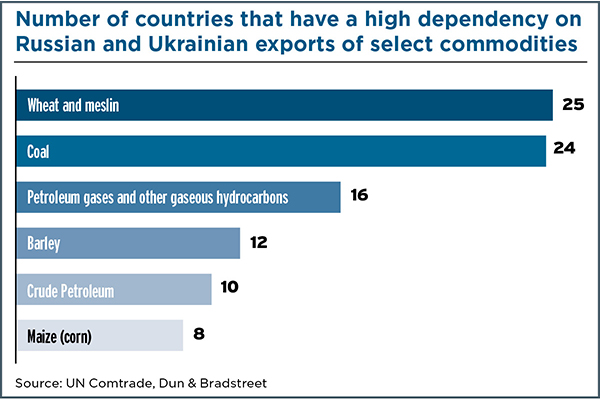
The report, which assesses the global business impact of the crisis, focuses on the businesses and countries that work with Russian and Ukrainian suppliers. Data compiled by the business intelligence provider shows that 25 countries heavily depend on Russia and Ukraine for a variety of commodities. In particular, at least 374,000 businesses worldwide rely on Russian suppliers—90% based in the United States—and at least 241,000 businesses rely on Ukrainian suppliers—93% based in the United States.
The most prominent commodities affected by the conflict include wheat and meslin, coal, and petroleum gases and other hydrocarbons. Of particular concern, the crisis threatens “to widely exacerbate Europe’s energy crisis,” according to the report, which notes that European gas storage levels are at a critically low 33% of capacity. Another concern is Germany placing a hold on the Nord Stream 2 gas pipeline as part of European Union sanctions on Russia.
The impact of the Russia-Ukraine crisis on the supply chain includes not only the disruption of trade routes but also increased freight costs and inaccessibility of critical raw materials. The sanctions on Russian companies issued by the United States, the UK, and the EU impact thousands of entities and “further cripple an already weakened global supply chain,” the report says.
